/zed/zed_node/left/camera_info
height: 360
width: 640
distortion_model: "plumb_bob"
D: (0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0)
K: (342.84136962890625, 0.0, 318.71136474609375, 0.0, 342.84136962890625, 185.68673706054688, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0)
R: (1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0)
P: (342.84136962890625, 0.0, 318.71136474609375, 0.0, 0.0, 342.84136962890625, 185.68673706054688, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0)
/zed/zed_node/left_raw/camera_info
height: 360
width: 640
distortion_model: "plumb_bob"
D: (-0.17287799715995789, 0.026074500754475594, 0.0, -9.226740075973794e-05, -0.0014505600556731224)
K: (350.6575012207031, 0.0, 318.9624938964844, 0.0, 350.6575012207031, 190.42774963378906, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0)
R: (1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0)
P: (350.6575012207031, 0.0, 318.9624938964844, 0.0, 0.0, 350.6575012207031, 190.42774963378906, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0)
/zed/zed_node/rgb/camera_info
height: 360
width: 640
distortion_model: "plumb_bob"
D: (0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0)
K: (342.84136962890625, 0.0, 318.71136474609375, 0.0, 342.84136962890625, 185.68673706054688, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0)
R: (1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0)
P: (342.84136962890625, 0.0, 318.71136474609375, 0.0, 0.0, 342.84136962890625, 185.68673706054688, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0)
/zed/zed_node/rgb_raw/camera_info
height: 360
width: 640
distortion_model: "plumb_bob"
D: (-0.17287799715995789, 0.026074500754475594, 0.0, -9.226740075973794e-05, -0.0014505600556731224)
K: (350.6575012207031, 0.0, 318.9624938964844, 0.0, 350.6575012207031, 190.42774963378906, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0)
R: (1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0)
P: (350.6575012207031, 0.0, 318.9624938964844, 0.0, 0.0, 350.6575012207031, 190.42774963378906, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0)/zed/zed_node/left/camera_info 높이 : 360 너비 : 640 distration_model : “plumb_bob”d : (0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0) k : (342.84136962890625, 0.0, 318.44474747474609375, 0, 342.42.42.84446464609375, , 1.0) R: (1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0) p: (342.84136962890625, 0.0, 318.71136474609375, 0.0, 0.0) /zed/zed_nodeera/40_left_info plumb_bob” D: (-0.17287799715995789, 0.026074500754475594, 0.0, -9.226740075973794e-05, -0.0014505600556731224) K: (350.6575012207031, 0.0, 318.9624938964844, 0.0, 350.6575012207031, 190.42774963378906, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0) R: (1.0 , 0.0, 0.0 , 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0) p : (350.6575012207031, 0.0, 318.9624938964844, 0.0, 350.6575012207031, 190.496378906, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0) /zed_nod : 360 -vering : 360 -vering : 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0) 케이: (342.84136962890625, 0.0, 318.71136474609375, 0.0, 342.84136962890625, 185.68673706054688, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0) r : (1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0) p : (342.84136962890625, 0.0, 318.7136474609375, 0.0, 34136962890625, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.005468 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0 /zed/zed_node/rgb_raw/camera_info 높이: 360 너비: 640 -9.226740075973794E -05, -0.0014505600556731224) K : (350.6575012207031, 0.0, 318.9624938964844, 0.0, 350.6575012207031.
$ roslaunch zed_wrapper zed.launchZed 카메라를 엽니다.
$ rostopic list주제 목록을 확인하십시오.
제가 체스판에서 가져온 카메라는 ZED의 왼쪽 카메라이니 왼쪽 카메라 정보는 주제로 검색해보세요.
/zed/zed_node/left/camera_info에서 Zed 매개 변수 값을 확인할 수 있습니다.
$ rostopic echo /zed/zed_node/left/camera_infoecho 명령어로 확인해보자.
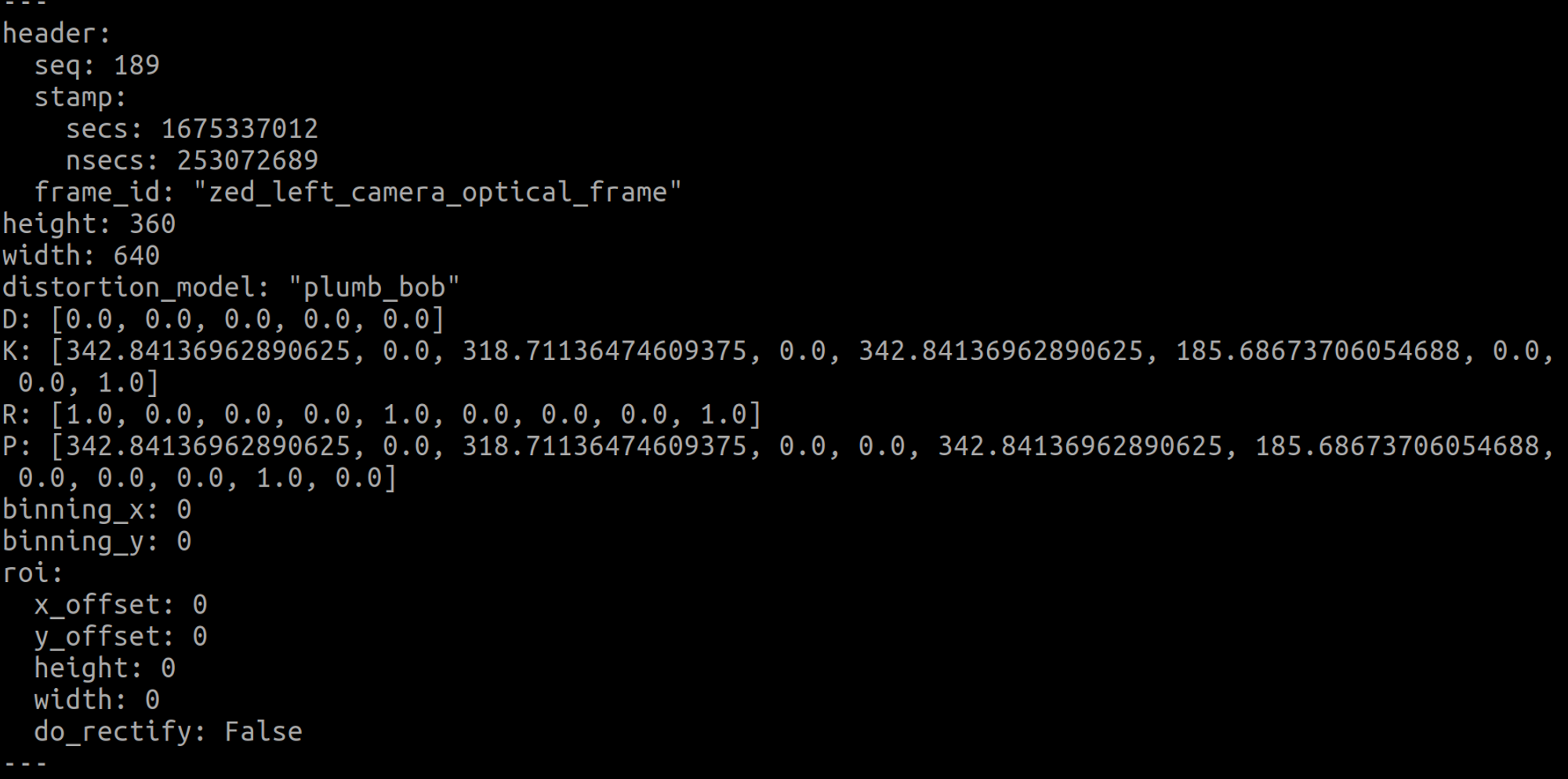
왜곡계수는 모두 0으로 확인
내부 매개변수는
케이: (342.84136962890625, 0.0, 318.71136474609375, 0.0, 342.84136962890625, 185.68673706054688, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0).
여기서 확인해야 할 것은 이미지의 해상도가 640과 360의 내부 매개변수라는 것입니다.
import cv2
import pyzed.sl as sl
def main():
# Create a Camera object
zed = sl.Camera()
# Create a InitParameters object and set configuration parameters
init_params = sl.InitParameters()
init_params.camera_resolution = sl.RESOLUTION.HD720 # Use HD1080 video mode
init_params.camera_fps = 30 # Set fps at 30
# Open the camera
err = zed.open(init_params)
if err != sl.ERROR_CODE.SUCCESS:
exit(1)
# Capture 50 frames and stop
i = 0
image = sl.Mat()
runtime_parameters = sl.RuntimeParameters()
while i < 1:
# Grab an image, a RuntimeParameters object must be given to grab()
if zed.grab(runtime_parameters) == sl.ERROR_CODE.SUCCESS:
# A new image is available if grab() returns SUCCESS
zed.retrieve_image(image, sl.VIEW.LEFT)
image_get = image.get_data()
cv2.imwrite("left_image.png", image_get)
timestamp = zed.get_timestamp(sl.TIME_REFERENCE.CURRENT) # Get the timestamp at the time the image was captured
print("Image resolution: {0} x {1} || Image timestamp: {2}\n".format(image.get_width(), image.get_height(),
timestamp.get_milliseconds()))
i = i + 1
# Close the camera
zed.close()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()위의 코드에서 해상도는 720으로 설정되어 있습니다.
따라서 left_image.png는 높이와 너비가 1280과 720인 이미지입니다.

이 이미지는 solvpnp 함수를 사용하여 카메라 외부 매개변수를 가져왔습니다.
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
// Read input image
cv::Mat im = cv::imread("/home/jaewoong/opencv_calibration/left_image.png");
// cv::resize( im, im, cv::Size( im.cols/2, im.rows/2 ), 0, 0, cv::INTER_AREA);
cv::resize( im, im, cv::Size( im.cols, im.rows ), 0, 0, cv::INTER_AREA);
// 2D image points. If you change the image, you need to change vector
std::vector<cv::Point2d> image_points;
image_points.push_back( cv::Point2d(653,472) ); // 1280, 720
image_points.push_back( cv::Point2d(716,469) );
image_points.push_back( cv::Point2d(686,489) );
image_points.push_back( cv::Point2d(654,514) );
image_points.push_back( cv::Point2d(724,515) );
// Left Mouth corner
// image_points.push_back( cv::Point2d(326.5,236) ); 1/2 640,360
// image_points.push_back( cv::Point2d(358,234.5) ); // Nose tip
// image_points.push_back( cv::Point2d(343,244.5) ); // Chin
// image_points.push_back( cv::Point2d(327,257) ); // Left eye left corner
// image_points.push_back( cv::Point2d(362,257.5) );
// 3D model points.
std::vector<cv::Point3d> model_points;
model_points.push_back(cv::Point3d(-1.0, 1.0, 0.0));
model_points.push_back(cv::Point3d(1.0, 1.0, 0.0)); // Nose tip
model_points.push_back(cv::Point3d(0.0, 0.0, 0.0)); // Chin
model_points.push_back(cv::Point3d(-1.0, -1.0, 0.0)); // Left eye left corner
model_points.push_back(cv::Point3d(1.0, -1.0, 0.0)); // Right eye right corner
// Left Mouth corner // Right mouth corner
// Camera internals
// double focal_length = im.cols; // Approximate focal length.
// Point2d center = cv::Point2d(im.cols/2,im.rows/2);
// cv::Mat camera_matrix = (cv::Mat_<double>(3,3) << 350.6575012207031, 0.0, 318.9624938964844, 0.0, 350.6575012207031, 190.42774963378906, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0); 640,360
// cv::Mat dist_coeffs = (cv::Mat_ <double>(4,1) << -0.17287799715995f, 0.026074500754475594f, 0.0, -9.226740075973794e-05); // Assuming no lens distortion
cv::Mat camera_matrix = (cv::Mat_<double>(3,3) << 712.54130286, 0.0, 639.67904873, 0.0, 714.09302856, 382.31150295, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0); // 1280,720
cv::Mat dist_coeffs = (cv::Mat_ <double>(4,1) << 0.01660484, -0.04549926, 0.00199781, -0.00092083); // Assuming no lens distortion
cout << "Camera Matrix " << endl << camera_matrix << endl ;
// Output rotation and translation
cv::Mat rotation_vector; // Rotation in axis-angle form
cv::Mat translation_vector;
// Solve for pose
cv::solvePnP(model_points, image_points, camera_matrix, dist_coeffs, rotation_vector, translation_vector);
// Project a 3D point (0, 0, 1000.0) onto the image plane.
// We use this to draw a line sticking out of the nose
vector<Point3d> nose_end_point3D;
vector<Point2d> nose_end_point2D;
nose_end_point3D.push_back(Point3d(0,0,10.0));
projectPoints(nose_end_point3D, rotation_vector, translation_vector, camera_matrix, dist_coeffs, nose_end_point2D);
for(int i=0; i < image_points.size(); i++)
{
circle(im, image_points(i), 3, Scalar(0,0,255), -1);
}
cv::line(im,image_points(2), nose_end_point2D(0), cv::Scalar(255,0,0), 2);
cout << "Rotation Vector " << endl << rotation_vector << endl;
cout << "Translation Vector" << endl << translation_vector << endl;
cout << nose_end_point2D << endl;
// Display image.
cv::imshow("Output", im);
cv::waitKey(0);
}위의 코드는 C++ 코드입니다. C++ 코드가 어떻게 생성되는지는 나중에 정리하겠습니다.
파라미터(1)에서 구한 ZED의 내부 파라미터 값은 해상도 640과 360을 기준으로 하기 때문에,
위에 저장된 이미지로 solvpnp를 실행해보니 값이 잘 나오지 않았습니다.
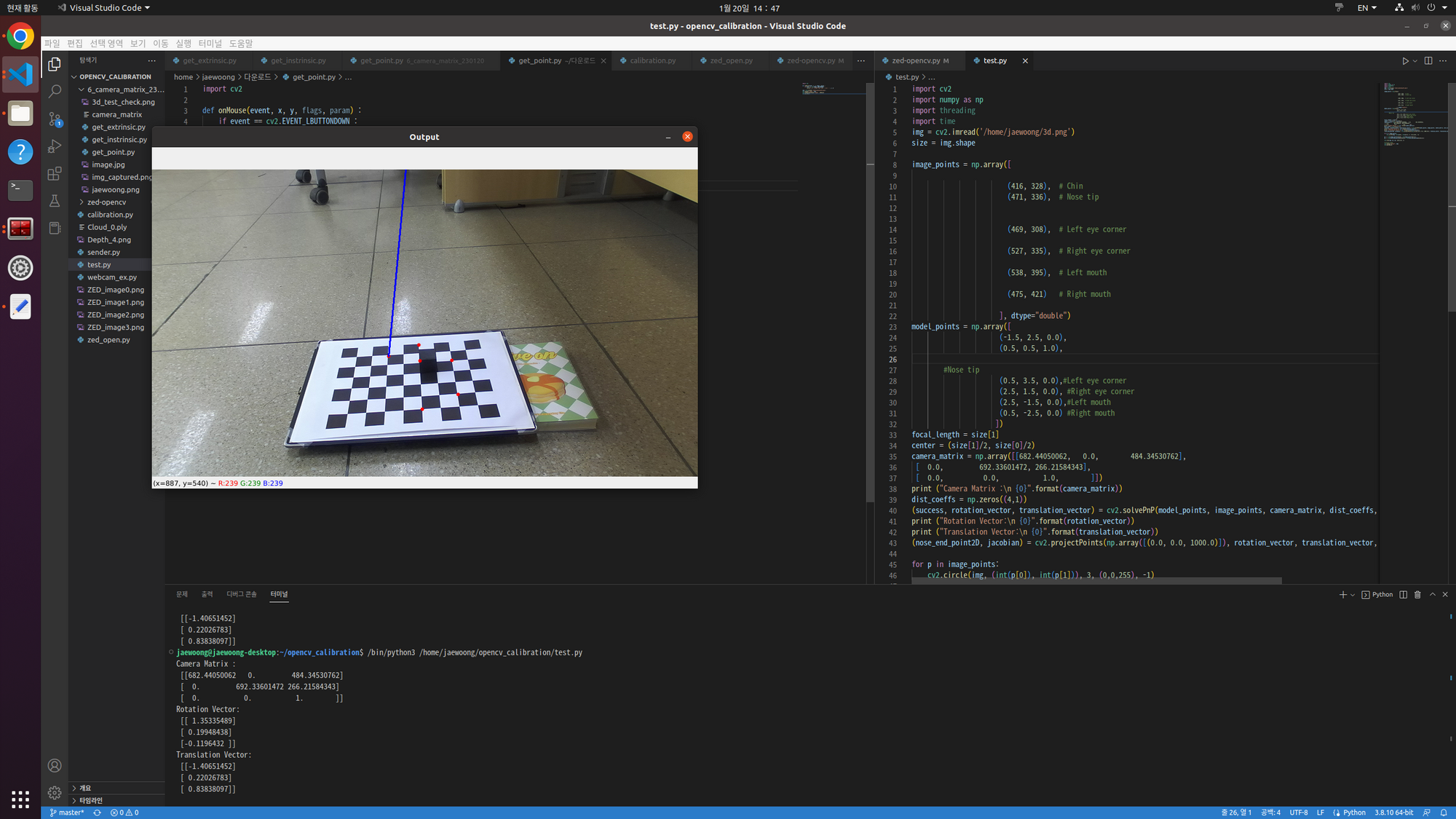
그래서 위의 코드에서
cv::resize( im, im, cv::Size( im.cols, im.rows ), 0, 0, cv::INTER_AREA);
cv::resize( im, im, cv::Size( im.cols/2, im.rows/2 ), 0, 0, cv::INTER_AREA);
크기 조정 기능을 사용하여 이미지를 작게 만들었습니다.
// image_points.push_back( cv::Point2d(326.5,236) ); 1/2 640,360
// image_points.push_back( cv::Point2d(358,234.5) ); // Nose tip
// image_points.push_back( cv::Point2d(343,244.5) ); // Chin
// image_points.push_back( cv::Point2d(327,257) ); // Left eye left corner
// image_points.push_back( cv::Point2d(362,257.5) );
마우스로 얻은 점수도 1/2을 주었다.
그러면 외부 매개변수 solvpnp의 값이 잘 나오는 것을 확인하였다.
지금까지 얻은 내부 파라미터 값은
/zed/zed_node/left/camera_info
height: 360
width: 640
distortion_model: "plumb_bob"
D: (0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0)
K: (342.84136962890625, 0.0, 318.71136474609375, 0.0, 342.84136962890625, 185.68673706054688, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0)
R: (1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0)
P: (342.84136962890625, 0.0, 318.71136474609375, 0.0, 0.0, 342.84136962890625, 185.68673706054688, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0)
/zed/zed_node/left_raw/camera_info
height: 360
width: 640
distortion_model: "plumb_bob"
D: (-0.17287799715995789, 0.026074500754475594, 0.0, -9.226740075973794e-05, -0.0014505600556731224)
K: (350.6575012207031, 0.0, 318.9624938964844, 0.0, 350.6575012207031, 190.42774963378906, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0)
R: (1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0)
P: (350.6575012207031, 0.0, 318.9624938964844, 0.0, 0.0, 350.6575012207031, 190.42774963378906, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0)
/zed/zed_node/rgb/camera_info
height: 360
width: 640
distortion_model: "plumb_bob"
D: (0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0)
K: (342.84136962890625, 0.0, 318.71136474609375, 0.0, 342.84136962890625, 185.68673706054688, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0)
R: (1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0)
P: (342.84136962890625, 0.0, 318.71136474609375, 0.0, 0.0, 342.84136962890625, 185.68673706054688, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0)
/zed/zed_node/rgb_raw/camera_info
height: 360
width: 640
distortion_model: "plumb_bob"
D: (-0.17287799715995789, 0.026074500754475594, 0.0, -9.226740075973794e-05, -0.0014505600556731224)
K: (350.6575012207031, 0.0, 318.9624938964844, 0.0, 350.6575012207031, 190.42774963378906, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0)
R: (1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0)
P: (350.6575012207031, 0.0, 318.9624938964844, 0.0, 0.0, 350.6575012207031, 190.42774963378906, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0)ROS 주제에서 얻은 매개 변수 값입니다.
내가 원하는 해상도로 이미지에 대한 매개변수 값을 찾으려고 합니다.
import cv2
import pyzed.sl as sl
def main():
# Create a Camera object
zed = sl.Camera()
# Create a InitParameters object and set configuration parameters
init_params = sl.InitParameters()
init_params.camera_resolution = sl.RESOLUTION.HD720 # Use HD720 video mode
init_params.camera_fps = 30 # Set fps at 30
# Open the camera
err = zed.open(init_params)
if err != sl.ERROR_CODE.SUCCESS:
exit(1)
# Capture 50 frames and stop
i = 0
image = sl.Mat()
runtime_parameters = sl.RuntimeParameters()
while True:
# Grab an image, a RuntimeParameters object must be given to grab()
if zed.grab(runtime_parameters) == sl.ERROR_CODE.SUCCESS:
# A new image is available if grab() returns SUCCESS
zed.retrieve_image(image, sl.VIEW.LEFT)
image_get = image.get_data()
cv2.imshow('color_image', image_get)
k = cv2.waitKey(1)
if ((k%256) == 32):
# cv2.cvtColor()
image_name = "./image_" + "{}.jpg".format(i)
cv2.imwrite(image_name, image_get)
print("save the image name{}".format(image_name))
i = i + 1
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
# Close the camera
zed.close()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()image(1), image(2) … 스페이스바를 누를 때마다. 이것은 이미지를 저장하는 코드입니다.
체스 판을 고치고 다른 관점에서 사진을 찍으십시오.
import cv2
import numpy as np
import os
import glob
# 체커보드의 차원 정의
CHECKERBOARD = (6,8) # 체커보드 행과 열당 내부 코너 수
criteria = (cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_EPS + cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_MAX_ITER, 30, 0.001)
# 각 체커보드 이미지에 대한 3D 점 벡터를 저장할 벡터 생성
objpoints = ()
# 각 체커보드 이미지에 대한 2D 점 벡터를 저장할 벡터 생성
imgpoints = ()
# 3D 점의 세계 좌표 정의
objp = np.zeros((1, CHECKERBOARD(0) * CHECKERBOARD(1), 3), np.float32)
objp(0,:,:2) = np.mgrid(0:CHECKERBOARD(0), 0:CHECKERBOARD(1)).T.reshape(-1, 2)
prev_img_shape = None
# 주어진 디렉터리에 저장된 개별 이미지의 경로 추출
images = glob.glob('/home/jaewoong/opencv_calibration/images/*.jpg')
for fname in images:
img = cv2.imread(fname)
# 그레이 스케일로 변환
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# 체커보드 코너 찾기
# 이미지에서 원하는 개수의 코너가 발견되면 ret = true
ret, corners = cv2.findChessboardCorners(gray,
CHECKERBOARD,
cv2.CALIB_CB_ADAPTIVE_THRESH + cv2.CALIB_CB_FAST_CHECK + cv2.CALIB_CB_NORMALIZE_IMAGE)
# 원하는 개수의 코너가 감지되면,
# 픽셀 좌표 미세조정 -> 체커보드 이미지 표시
if ret == True:
objpoints.append(objp)
# 주어진 2D 점에 대한 픽셀 좌표 미세조정
corners2 = cv2.cornerSubPix(gray, corners, (11,11),(-1,-1), criteria)
imgpoints.append(corners2)
# 코너 그리기 및 표시
img = cv2.drawChessboardCorners(img, CHECKERBOARD, corners2, ret)
cv2.imshow('img',img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
h,w = img.shape(:2) # 480, 640
# 알려진 3D 점(objpoints) 값과 감지된 코너의 해당 픽셀 좌표(imgpoints) 전달, 카메라 캘리브레이션 수행
ret, mtx, dist, rvecs, tvecs = cv2.calibrateCamera(objpoints, imgpoints, gray.shape(::-1), None, None)
print("Camera matrix : \n") # 내부 카메라 행렬
print(mtx)
print("dist : \n") # 렌즈 왜곡 계수(Lens distortion coefficients)
print(dist)
# print("rvecs : \n") # 회전 벡터
# print(rvecs)
# print("tvecs : \n") # 이동 벡터
# print(tvecs)
이미지 파일의 모든 JPG 파일에 대해 보정이 수행됩니다.
이미지 보정
카메라 매트릭스:
((712.54130286 0.639.67904873) (0.714.09302856 382.31150295) (0.0.1.))
거리:
(( 0.01660484 -0.04549926 0.00199781 -0.00092083 0.03364123))
이렇게 내부 파라미터 값이 나왔는데,
위의 내부 매개변수 값을 solvpnp 코드에 입력하여 외부 매개변수 값을 가져옵니다.
solvepnp 함수를 사용하는 C++ 코드입니다.
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
// Read input image
cv::Mat im = cv::imread("/home/jaewoong/opencv_calibration/left_image.jpg");
// cv::resize( im, im, cv::Size( im.cols/2, im.rows/2 ), 0, 0, cv::INTER_AREA);
cv::resize( im, im, cv::Size( im.cols, im.rows ), 0, 0, cv::INTER_AREA);
// 2D image points. If you change the image, you need to change vector
std::vector<cv::Point2d> image_points;
image_points.push_back( cv::Point2d(485,533) ); // 1280, 720
image_points.push_back( cv::Point2d(604,537) );
image_points.push_back( cv::Point2d(602,621) );
image_points.push_back( cv::Point2d(457,618) );
image_points.push_back( cv::Point2d(538,574) );
// 3D model points.
std::vector<cv::Point3d> model_points;
model_points.push_back(cv::Point3d(-2.0, 2.0, 0.0));
model_points.push_back(cv::Point3d(2.0, 2.0, 0.0)); // Nose tip
model_points.push_back(cv::Point3d(2.0, -2.0, 0.0)); // Chin
model_points.push_back(cv::Point3d(-2.0, -2.0, 0.0)); // Left eye left corner
model_points.push_back(cv::Point3d(0.0, 0.0, 0.0)); // Right eye right corner
// Left Mouth corner // Right mouth corner
// Camera internals
// double focal_length = im.cols; // Approximate focal length.
// Point2d center = cv::Point2d(im.cols/2,im.rows/2);
// cv::Mat camera_matrix = (cv::Mat_<double>(3,3) << 350.6575012207031, 0.0, 318.9624938964844, 0.0, 350.6575012207031, 190.42774963378906, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0); 640,360
// cv::Mat dist_coeffs = (cv::Mat_ <double>(4,1) << -0.17287799715995f, 0.026074500754475594f, 0.0, -9.226740075973794e-05); // Assuming no lens distortion
cv::Mat camera_matrix = (cv::Mat_<double>(3,3) << 712.54130286, 0.0, 639.67904873, 0.0, 714.09302856, 382.31150295, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0); // 1280,720
cv::Mat dist_coeffs = (cv::Mat_ <double>(4,1) << 0.01660484, -0.04549926, 0.00199781, -0.00092083); // Assuming no lens distortion
cout << "Camera Matrix " << endl << camera_matrix << endl ;
// Output rotation and translation
cv::Mat rotation_vector; // Rotation in axis-angle form
cv::Mat translation_vector;
// Solve for pose
cv::solvePnP(model_points, image_points, camera_matrix, dist_coeffs, rotation_vector, translation_vector);
// Project a 3D point (0, 0, 1000.0) onto the image plane.
// We use this to draw a line sticking out of the nose
vector<Point3d> nose_end_point3D;
vector<Point2d> nose_end_point2D;
nose_end_point3D.push_back(Point3d(0,0,5.0));
projectPoints(nose_end_point3D, rotation_vector, translation_vector, camera_matrix, dist_coeffs, nose_end_point2D);
for(int i=0; i < image_points.size(); i++)
{
circle(im, image_points(i), 3, Scalar(0,0,255), -1);
}
cv::line(im,image_points(4), nose_end_point2D(0), cv::Scalar(255,0,0), 2);
cout << "Rotation Vector " << endl << rotation_vector << endl;
cout << "Translation Vector" << endl << translation_vector << endl;
cout << nose_end_point2D << endl;
// Display image.
cv::imshow("Output", im);
cv::waitKey(0);
}
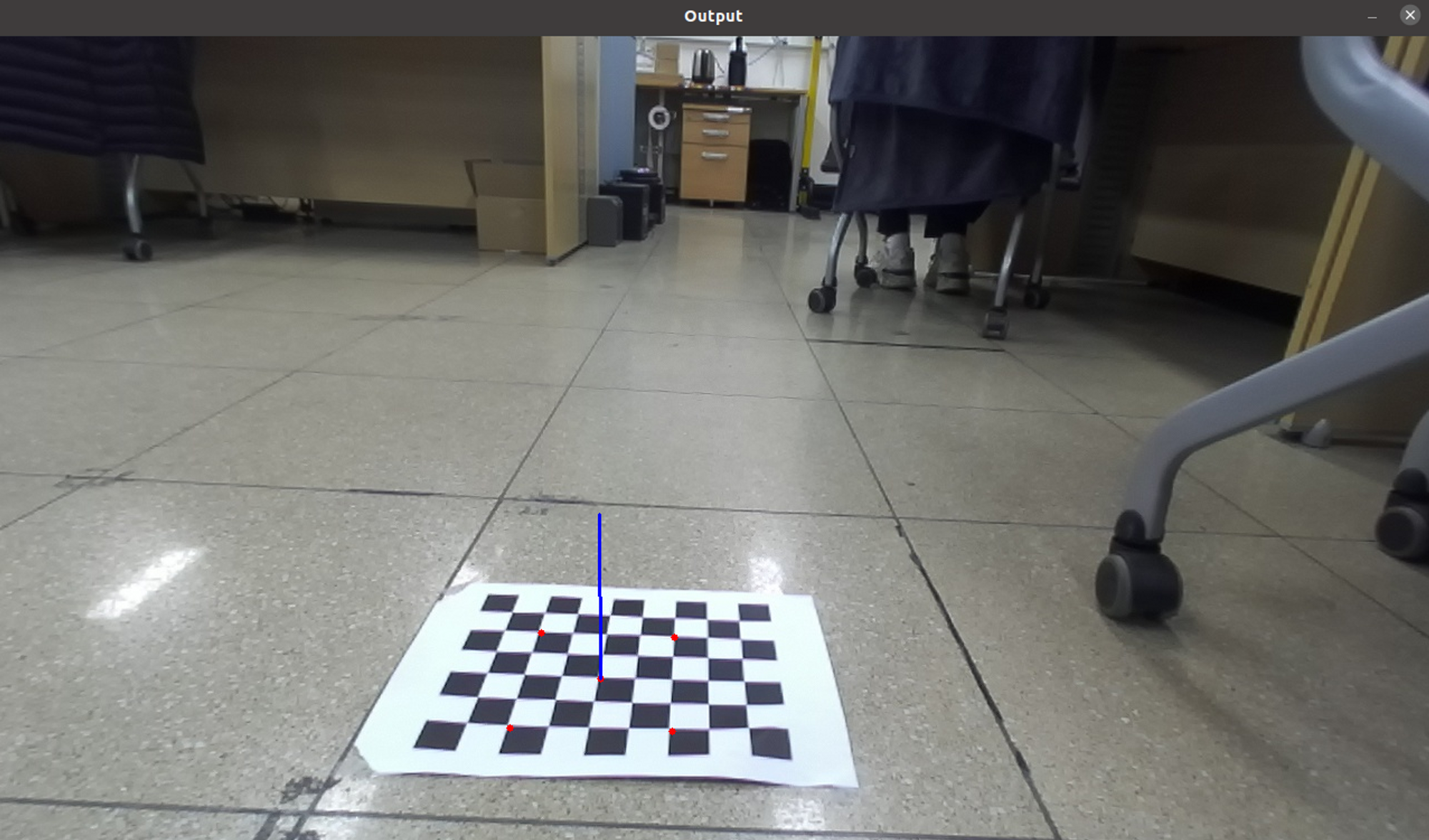

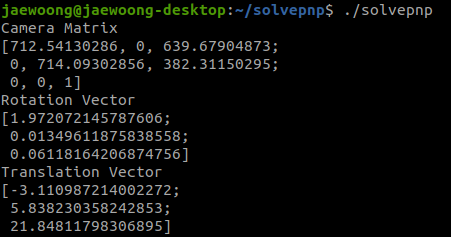
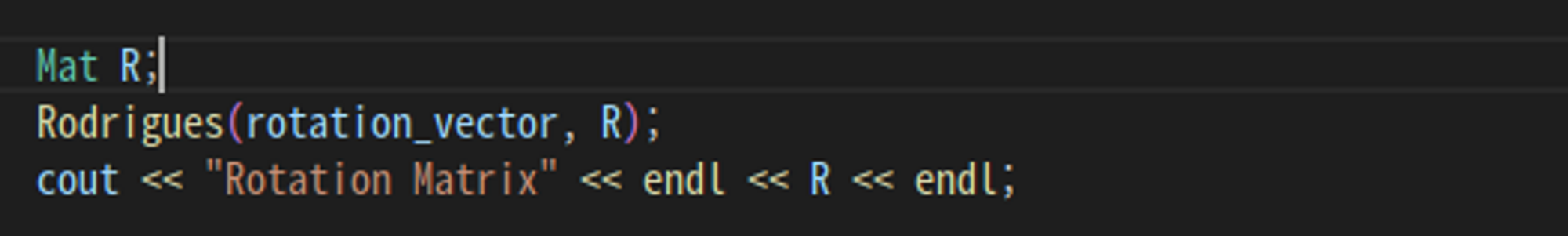
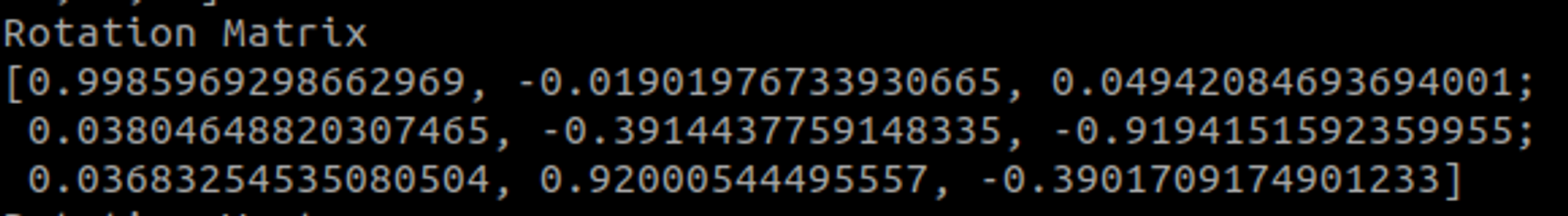
카메라의 외부 매개변수인 회전 벡터와 평행이동 벡터가 나온 것을 볼 수 있습니다.
원하는 외부 매개변수인 회전은 3×3 형식이어야 합니다.
회전 행렬을 찾기 위해 Rodrigues 표현식을 사용합니다.